The following are general sensitivity patterns. Resistance can still occur, culture sensitivities should always be considered, and sites of infections or guidelines are not taken into account. See "Bugs & Tips" for recommendations about specific pathogens or "Guidelines" for treatment approaches.
NATURAL PENICILLINS (penicillin G, penicillin VK)
ANTI-STAPHYLOCOCCAL PENICILLINS (nafcillin, dicloxacillin)
AMINOPENICILLINS (ampicillin, amoxicillin)
ANTI-PSEUDOMONAL PENICILLINS (piperacillin/tazobactam)
FIRST GENERATION CEPHALOSPORINS (Cefazolin, Cephalexin)
SECOND GENERATION CEPHALOSPORINS (cefuroxime and cefoxitin, the latter also active against anaerobes)
MONOBACTAMS (aztreonam)
VANCOMYCIN
DAPTOMYCIN
TETRACYCLINES (tetracycline, doxycycline, minocycline)
MACROLIDES (azithromycin, clarithromycin, erythromycin)
AMINOGLYCOSIDES (amikacin, tobramycin, gentamicin)
STREPTOGRAMINS (quinupristin/dalfopristin)
OXAZOLIDINONES (linezolid)
CLINDAMYCIN
FLUOROQUINOLONES (levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin)
METRONIDAZOLE
SULFONAMIDES (sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim)
NITROFURANTOIN
- G (+) Coverage
- Penicillin-sensitive strep pneumo
- Group A, B, C, G strep
- Viridans strep
- Susceptible enterococcus strains
- G (-) Coverage
- Neisseria
- Anaerobes
- Mostly above the diaphragm
- Clostridium (not difficile)
- Other
- Trepnema pallidum (Syphilis)
ANTI-STAPHYLOCOCCAL PENICILLINS (nafcillin, dicloxacillin)
- G (+) Coverage
- MSSA
- Group A, B, C, G strep
- Viridans strep
- Note: Do not use for any enterococcus infections
AMINOPENICILLINS (ampicillin, amoxicillin)
- G (+) Coverage
- Same as natural penicillins
- Penicillin-sensitive strep pneumo
- Group A, B, C, G strep
- Viridans strep
- Susceptible enterococcus strains
- Same as natural penicillins
- G (-) Coverage
- Salmonella
- Shigella
- Some E. coli
- Beta-lactamase-negative H. influenzae
- Proteus mirabilis
- Note: Adding a beta lactamase inhibitor adds coverage against beta-lactamase producing organisms. So MSSA, Bacteroides, E. Coli, Klebsiella, and Proteus may be susceptible. Remember that resistance may be due to mechanisms other than beta lactamase production, mechanisms where a beta lactam/beta lactamase inhibitor may not be helpful.
ANTI-PSEUDOMONAL PENICILLINS (piperacillin/tazobactam)
- G (+) Coverage
- Same as natural penicillins
- Penicillin-sensitive strep pneumo
- Group A, B, C, G strep
- Viridans strep
- Susceptible enterococcus strains
- Same as natural penicillins
- G (-) Coverage
- Salmonella
- Shigella
- E. coli
- Beta-lactamase-negative H. influenzae
- Enterococcus
- Pseudomonas
- Serratia
- Klebsiella
- Note: Adding a beta lactamase inhibitor adds coverage against beta-lactamase producing organisms. So MSSA, Bacteroides, E. Coli, Klebsiella, and Proteus may be susceptible. Remember that resistance may be due to mechanisms other than beta lactamase production, mechanisms where a beta lactam/beta lactamase inhibitor may not be helpful.
FIRST GENERATION CEPHALOSPORINS (Cefazolin, Cephalexin)
- G (+) Coverage
- MSSA
- penicillin-sensitive strep pneumo
- Group A, B, C, G strep
- Viridans strep
- G (-) Coverage
- E. Coli
- Some strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Some strains of Proteus mirabilis
SECOND GENERATION CEPHALOSPORINS (cefuroxime and cefoxitin, the latter also active against anaerobes)
- Compared to first generation, slightly less active against G(+) organisms, but more active against G(-) organisms
- G (+) Coverage
- MSSA
- penicillin-sensitive strep pneumo
- Group A, B, C, G strep
- Viridans strep
- G (-) Coverage
- E. Coli
- Proteus mirabilis
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Neisseria
- Moraxella
- Anaerobes
- Of the formulary agents, only cefoxitin possesses anaerobic activity
- Bacteroides
- Clostridium (non-difficile)
- Of the formulary agents, only cefoxitin possesses anaerobic activity
- G (+) Coverage
- G (+) Coverage
- MSSA
- Strep pneumo
- Group A, B, C, G strep
- Viridans strep
- G (-) Coverage
- E. Coli
- Proteus mirabilis
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Neisseria
- Moraxella
- Citrobacter
- Enterobacter
- Serratia
- G (+) Coverage
- MSSA
- Strep pneumo
- Group A, B, C, G strep
- Viridans strep
- G (-) Coverage
- E. Coli
- Proteus
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Neisseria
- Moraxella
- Citrobacter
- Enterobacter
- Acinetobacter (see organism page)
- Serratia
- Broadest spectrum agents
- Active against G(+), G(-), aerobes, and anaerobes
- Pseudomonas: Meropenem active, ertapenem is not active
- NOT ACTIVE against MRSA, VRE, methicillin-resistant CoNS
MONOBACTAMS (aztreonam)
- No G(+) activity, no anaerobic activity
- G(-) Coverage:
- E. Coli
- Klebsiella
- Pseudomonas
- Proteus
- Serratia
- H. influenzae
- Moraxella
- Enterobacter
- Citrobacter
- Providencia
- Morganella
- Salmonella
- Shigella
VANCOMYCIN
- G(+) Coverage:
- MSSA
- MRSA
- CoNS
- Strep pneumo (including penicillin-resistant strains)
- Viridans strep
- Group A, B Strep
- Enterococcus
- Corynebacterium
- Listeria
- Actinomyces
- Clostridium (including difficile)
- Peptococcus
- Peptostreptococcus
- No G(-) activity
DAPTOMYCIN
- Broad G(+) agent, spectrum includes:
- MRSA
- VRE (both faecium and faecalis)
- Broad G(-) agent, spectrum includes:
- E. Coli
- Klebsiella
- Enterobacter
- Pseudomonas
- Acinetobacter
- NOT ACTIVE against Proteus, Providencia, and Serratia
TETRACYCLINES (tetracycline, doxycycline, minocycline)
- G(+) Coverage
- MSSA
- Some MRSA (see "Bugs & Tips& section)
- Resistance common in G(-) pathogens
- Some anaerobic activity
- Atypical Coverage
- Mycoplasma
- Chlamydia
- Rickettsiae
- Broad G(+) activity, including MRSA, VRE
- Broad G(-) activity with some limitations:
- Active against ESBL pathogens and Acinetobacter
- NOT ACTIVE against Morganella, Proteus, Providencia, Pseudomonas
- Anaerobic and atypical coverage similar to tetracycline class
- Cross-resistance not typical between tetracyclines and tigecycline
MACROLIDES (azithromycin, clarithromycin, erythromycin)
- Used for respiratory sites of infection rather than non-respiratory sites
- G(+) Coverage:
- MSSA, but see "Bugs & Tips" for preferred agents
- Streptococcus species, but see "Bugs & Tips" for preferred agents
- G(-) Coverage Limited:
- H. influenzae
- Moraxella
- Atypical Coverage
- Chlamydia
- Mycoplasma
- Legionella
AMINOGLYCOSIDES (amikacin, tobramycin, gentamicin)
- G(+) activity only in combination with a cell wall agent!
- MSSA
- CoNS
- Viridans Strep
- Enterococcus (gentamicin)
- G(-) Coverage:
- E. Coli
- Klebsiella
- Proteus
- Pseudomonas (tobramycin more active than gentamicin)
- Acinetobacter
- Citrobacter
- Enterobacter
- Morganella
- Providencia
- Serratia
- Salmonella
- Shigella
- Notable adverse effects: ototoxicity, NVD, vertigo, nystagmus, vestibular disturbance, nephrotoxicity (usually reversible, typically after 5 or more days of treatment), neuromuscular blockade reversible via calcium gluconate
STREPTOGRAMINS (quinupristin/dalfopristin)
- Broad G(+) coverage, including:
- MRSA
- Enterococcus faecium (including VRE)
- NOT ACTIVE against Enterococcus faecalis
- Strep
- Limited G(-) coverage
- Neisseria
- Moraxella
- Notable adverse effects: NVD, hyperbilirubinemia, myalgias, arthralgias
OXAZOLIDINONES (linezolid)
- Broad G(+) activity, including:
- MRSA
- VRE (both E. faecium and E. faecalis)
- No significant G(-) activity
- Atypical coverage:
- Mycoplasma
- Chlamydia
- Legionella
- Notable adverse effects: NVD, reversible myelosuppression (typically with prolonged treatment, e.g. >2 weeks), MAOI activity (interactions), peripheral and optic nerve neuropathy
CLINDAMYCIN
- G(+) coverage:
- MSSA
- MRSA (see "Bugs & Tips")
- Strep pneumo
- Viridans strep
- NOT ACTIVE against Enterococcus
- G(-) coverage poor
- Anaerobes (Metronidazole has better anaerobic activity than clindamycin)
- "Mostly above the diaphragm", upper GI and higher
- Some Bacteroides
- Peptostreptococcus
- Actinomyces
- Prevotella
- Fusobacterium
- Non-difficile Clostridium
- Notable adverse effects: NVD, dyspepsia, C. difficile infection, rare hepatotoxicity with increasing transaminases
FLUOROQUINOLONES (levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin)
- G+ Coverage:
- MSSA (but poor agent for this purpose, see "Bugs & Tips" section for more info)
- Strep pneumo (ONLY levofloxacin, moxifloxacin, and gemifloxatin; NOT ciprofloxacin)
- Viridans strep
- Limited activity against enterococcus
- G(-) Coverage:
- Ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin have better activity than moxifloxacin
- Enterobacteriaceae
- H. influenzae
- Moraxella
- Neisseria
- Pseudomonas (ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin only; NOT moxifloxacin)
- Atypicals:
- Excellent activity, including pathogens like Legionella, Chlamydia, and Mycoplasma
- Other:
- Active against Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Bacillus anthracis
- Notes: great penetration into tissues, including prostate, liver, soft tissue, lung, skin, bone, urinary tract (levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin); minimal CSF penetration
METRONIDAZOLE
- Anaerobic Bacterial Coverage:
- All Bacteroides species
- Fusobacterium
- Prevotella
- All Clostridium species
- H. pylori
- Anaerobic Protozoa Coverage:
- Trichomonas vaginalis
- Entamoeba histolytica
- Giardia lamblia
- Gardnerella vaginalis
- Comments: drug interaction with warfarin, can lead to increased INR
SULFONAMIDES (sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim)
- G(+) Coverage:
- MSSA
- Some MRSA (skin infections, see "Bugs & Tips" for more info)
- Some Strep species
- G(-) Coverage:
- E. Coli (confirm sensitivities)
- Stenotrophomonas (drug of choice)
- Moraxella
NITROFURANTOIN
- Only used in uncomplicated UTIs, typically for pathogens like:
- E. Coli
- Staph. saprophyticus
- Note: Only effective in patients with CrCl > 50 mL/min, otherwise does not achieve high enough concentrations to work!
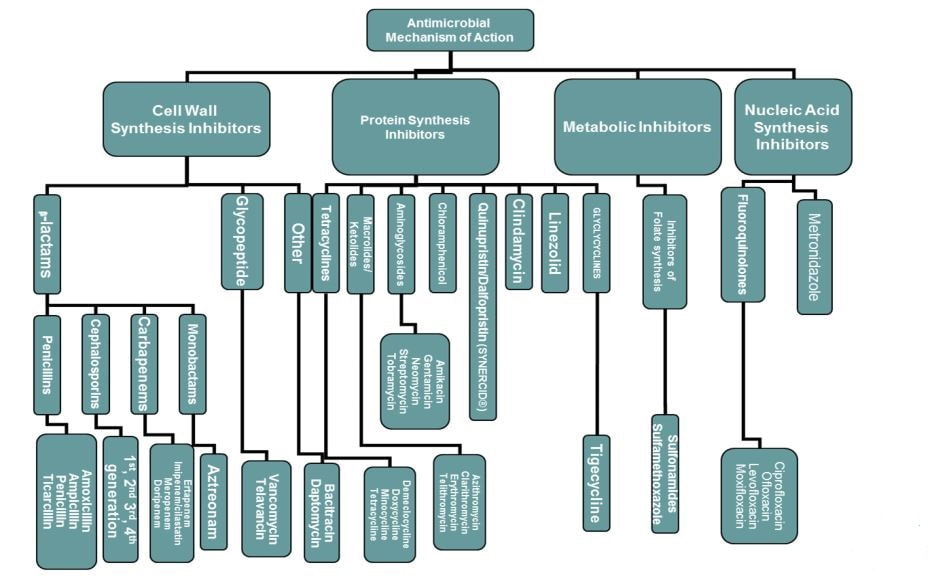
The following chart, courtesy of SIDP, gives a visual representation of the mechanisms of action of the bacterial anti-infectives.