UPDATES
September 2023: Updates to testing, dosing for initial episode and recurrences, and prophylaxis if known c. diff history.
December 2019: Updated treatment algorithm categorization and dosing
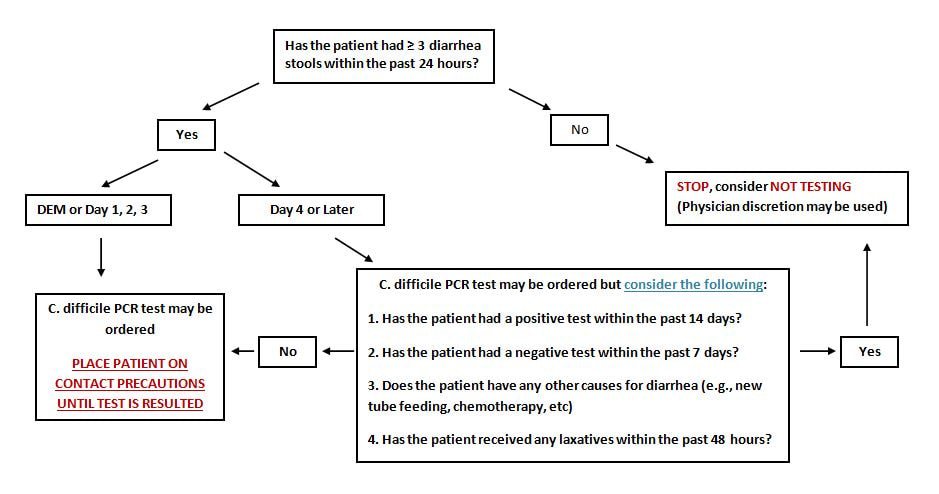
October 2018: GVH created a C-difficile testing decision tree to reduce the incidence of inappropriate stool sampling, see below
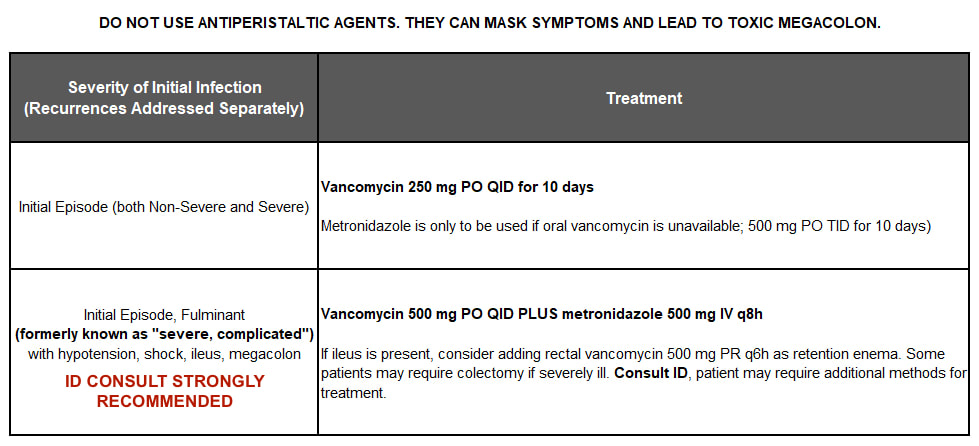
April 2018: IDSA updated its guidelines, and GVH's protocol below reflects those changes. Highlights include oral vancomycin now being the treatment of choice, oral metronidazole no longer being used in C. difficile infection of any severity, and IV metronidazole being reserved for combination therapy with vancomycin 500 mg PO for severe complicated cases, which are now referred to as "fulminant"
September 2023: Updates to testing, dosing for initial episode and recurrences, and prophylaxis if known c. diff history.
December 2019: Updated treatment algorithm categorization and dosing
October 2018: GVH created a C-difficile testing decision tree to reduce the incidence of inappropriate stool sampling, see below
April 2018: IDSA updated its guidelines, and GVH's protocol below reflects those changes. Highlights include oral vancomycin now being the treatment of choice, oral metronidazole no longer being used in C. difficile infection of any severity, and IV metronidazole being reserved for combination therapy with vancomycin 500 mg PO for severe complicated cases, which are now referred to as "fulminant"
TESTING
- See GVH decision tree below
- Test only when patient has diarrhea (unformed stool), unless ileus due to C. difficile is suspected
- Do not test asymptomatic patients or test for cure. Patients may test positive for up to 6 weeks following treatment of C. difficile.
- Not recommended to repeat test during the same episode of diarrhea. It has been found to have limited value.
- GVH has PCR testing and EIA toxin testing. If a patient tests positive for PCR, an EIA toxin test will be done automatically.
- If a patient is PCR positive and EIA toxin positive, that indicates active infection.
- If a patient is PCR positive and EIA toxin negative, the patient may be a c. diff carrier or recently recovered from a c.diff infection. It is not generally recommended to treat these patients.
initial episode
If the antibiotic causing the C. diff infection cannot be stopped at the time C. diff diagnosis is made because the patient must continue treatment for a different infection, continue the C. diff treatment for 1 week after the final dose of the causative antibiotic.
PROPHYLAXIS FOR C. DIFF
RECURRENCE
RISK FACTORS
FACILITIES
ANTIBIOTICS
PROTON PUMP INHIBITORS
REFERENCES
PROPHYLAXIS FOR C. DIFF
- If the patient is a known C. diff carrier or has a prior history of C. diff and requires antibiotics for an infection, give vancomycin 125 mg PO BID while taking antibiotics and for 1 week after stopping them.
RECURRENCE
- 1st Recurrence
- If metronidazole was used for the initial episode, give vancomycin 250 mg PO QID for 10 days
- If vancomycin was used for the initial episode, give prolonged vancomycin PO taper or pulse regimen (250 mg PO QID for 10-14 days, BID for 7 days, daily for 7 days, and then every 2 to 3 days for 2-8 weeks)
- 2nd or Subsequent Recurrence
- Consult infectious disease for treatment. May require alternate methods for treatment.
RISK FACTORS
- Advanced age (>64 years )
- Duration of hospitalization
- Risk increased with longer length of stay
- Exposure to antimicrobial agents
- Risk increased the longer the patient is on the antimicrobial agent
- Risk increased when patient is on more than one antimicrobial agent
- Cancer chemotherapy/immunosuppressed
- Gastrointestinal surgery, manipulation of GI tract, tube feeding
- Questionable - use of PPI and H2 blockers
FACILITIES
- Healthcare workers and visitors should wear gowns and gloves before entering a patient’s room with C. difficile.
- Hand hygiene is extremely important. Wash with soap and water before and after contact with infected patient. Alcohol based hand sanitizers are not recommended as the C. difficile spores are resistant to killing by alcohol.
- Keep patient in a private room under contact precautions
- Contact precautions must be maintained for duration of the diarrhea
- It is not recommended to test asymptomatic carriers or to treat those identified individuals for infection control purposes.
- Use chlorine-containing cleaning agents or other sporicidal agents
ANTIBIOTICS
- Minimize frequency, duration, and number of antibiotics whenever possible to prevent C. difficile.
- If patient is on antibiotics when C. difficile is identified, try to deescalate the antibiotics or discontinue the inciting antibiotic totally when appropriate to help decrease chance of recurrence.
- Antibiotics that are not implicated in C. difficile as often are vancomycin, aminoglycosides, macrolides, sulfonamides, and tetracycline.
- As mentioned previously, if the antibiotic causing the C. diff infection cannot be stopped at the time C. diff diagnosis is made because the patient must continue treatment for a different infection, continue the C. diff treatment for 1 week after the final dose of the causative antibiotic.
PROTON PUMP INHIBITORS
- It is recommended that PPI’s be stopped on patients with C. difficile or a history of C. difficile if possible.
REFERENCES
- Johnson S., Lavergne V, Skinner AM, et al. Clinical Practice Guideline by the Infectious Disease Society of America (IDSA) and Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA): 2021 Focused Update Guidelines on Management of Clostridioides difficile Infection in Adults. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2021; 73: 1029-1044.
- Kelly CP. Clostridium difficile infection in adults: Treatment and Prevention. In UpToDate, Calderwood SB (Ed), UpToDate, Waltham (MA): UpToDate, Inc.; 2023 [cited 2023 September 25]. Available from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/clostridioides-difficile-infection-in-adults-treatment-and-prevention?search=clostridium%20difficile%20treatment&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1~150&usage_type=default&display_rank=1#H1540545612.