empiric treatment algorithms
CLINICAL NOTES
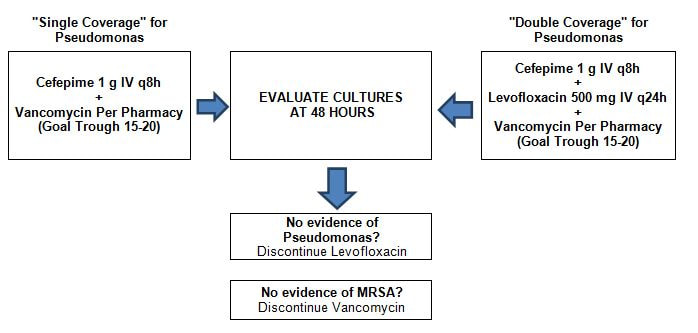
DO YOU NEED ONE OR TWO AGENTS FOR PSEUDOMONAS COVERAGE?
DO YOU NEED ONE OR TWO AGENTS FOR PSEUDOMONAS COVERAGE?
- Empiric Pseudomonas coverage with two antipseudomonal agents from two different classes is recommended for patients with any of the following:
- A risk factor for MDR pathogens
- Patient requires ventilator support due to HAP and septic shock
- ARDS preceding VAP
- Five or more days of hospitalization prior to occurrence of VAP
- Acute renal replacement therapy prior to VAP onset
- Presence of bronchiectasis or cystic fibrosis
- OR, patients in units where >10% of gram-negative isolates are resistant to an agent being considered for monotherapy
- Empiric Pseudomonas coverage with a single anti-pseudomonal agent is recommended for patients without risk factors for MDR pathogens who are being treated in ICU where ≤10% of gram-negative isolates are resistant to the agent being considered for monotherapy. However, aminoglycosides in particular are not recommended as the monotherapy choice.
- Empiric MRSA coverage with vancomycin recommended since >20% of S. aureus at GVH is MRSA
- Once the pathogen is identified, de-escalate therapy to a single agent
- If no pathogen is isolated, consider whether there is evidence of MRSA or Pseudomonas. If not, narrow therapy to prevent putting patients at risk for multidrug –resistant pathogens and complications like C. difficile infection
- Metronidazole may be added if anaerobic coverage is needed where aspiration is the source of PNA
- For Acinetobacter infections, ampicillin/sulbactam or carbapenem are preferred if susceptible
- Allergies
- If true penicillin allergy, your empiric regimen should be: Vancomycin + Levofloxacin + Aztreonam
- If true fluoroquinolone allergy, your empiric regimen should be: Vancomycin + Cefepime + Aztreonam + Azithromycin
DEFINITIONS
RECOMMENDED DIAGNOSTICS
PATHOGENS
DIAGNOSIS AND CLINICAL TEST COMMENTARY
DURATION OF TREATMENT
REFERENCES
- HAP (Healthcare Acquired Pneumonia)
- Onset occurs 48 hours or more after admission
- VAP (Ventilator Associated Pneumonia)
- Onset greater than 48 hours after endotracheal intubation; patients with HAP who are intubated should be managed as having VAP.
RECOMMENDED DIAGNOSTICS
- Blood cultures x 2
- Sputum or bronchial cultures
- Urine Legionella antigen (recommended for ICU patients, failure of outpatient antibiotics, active alcohol abuse)
PATHOGENS
- According to national data, most common pathogens: S. aureus (20-30%), Pseudomonas (10-20%), enteric gram negatives (20-40%), Acinetobacter (5-10%)
DIAGNOSIS AND CLINICAL TEST COMMENTARY
- CPIS (Clinical Pulmonary Infection Score)
- Not recommended to guide antibiotic therapy since specificity and sensitivity not high enough
- Procalcitonin (PCT)
- Strong recommendation to use clinical criteria alone, rather than using PCT plus clinical criteria, to decide whether to initiate antibiotics
- Weak recommendation to use PCT plus clinical criteria, rather than clinical criteria alone, to guide discontinuation of antibiotics
DURATION OF TREATMENT
- 7 days, but consider clinical situation and regularly evaluate whether antibiotics still needed
- Pseudomonas or Acinetobacter infections in particular may require 14 days
REFERENCES
- Clin Infect Dis 2016; 63: e61-e111